6.5.3.2 Koupleless Third-party Package Patch Guide
Principle of Koupleless Third-party Package Patches
Koupleless is an architecture designed for multiple applications, whereas traditional middleware might only consider a single application scenario. Therefore, in some behaviors, it cannot accommodate the coexistence of multiple applications, leading to issues such as shared variable pollution, classLoader loading anomalies, and unexpected class judgments.
Therefore, when using Koupleless middleware, we need to apply patches to some potential issues, overriding the original middleware implementation, so that open-source middleware can also be compatible with a multi-application model.
‼️ Version Requirements: koupleless-base-build-plugin
- jdk8: >= 1.3.3
- jdk17: >= 2.2.8
Currently, the principle of Koupleless third-party package patches taking effect is:
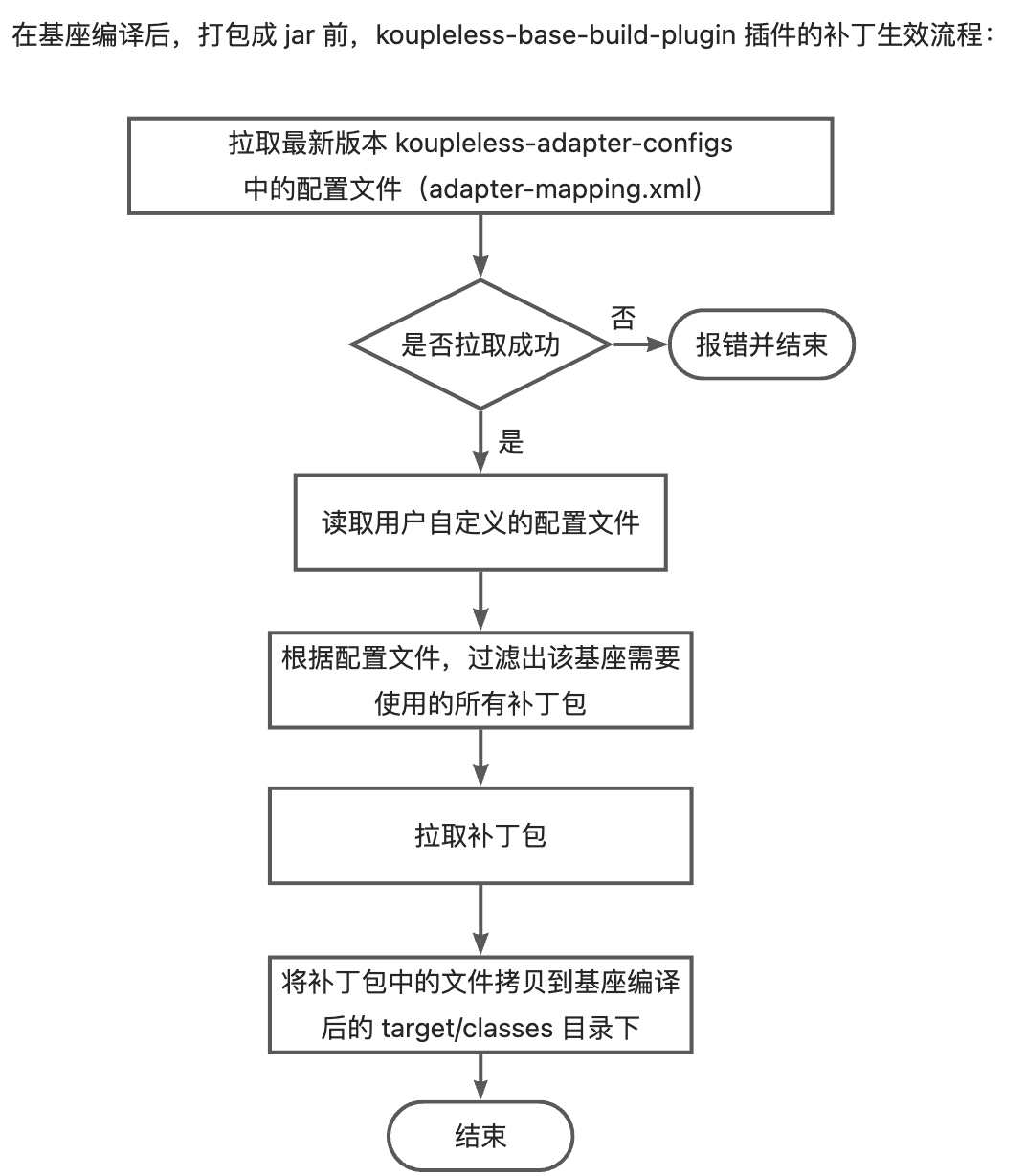
- After the base compilation and before packaging, the koupleless-base-build-plugin plugin will obtain the adapter configuration file, which describes the
middleware dependencies within the version rangethat use the patch packages, for example:
version: 1.2.3
adapterMappings:
- matcher:
groupId: org.springframework.boot
artifactId: spring-boot
versionRange: "[2.5.1,2.7.14]"
adapter:
artifactId: koupleless-adapter-spring-boot-logback-2.7.14
groupId: com.alipay.sofa.koupleless
The meaning of this configuration file is: When the base depends on org.springframework.boot:spring-boot versions within the range [2.5.1, 2.7.14], then use the koupleless-adapter-spring-boot-logback-2.7.14 patch package version 1.2.3.
- Obtain all dependencies used by the base, filter out all the patch packages required by the base according to the adapter configuration file;
- Pull the patch packages and copy the files from the patch packages to the target/classes directory after the base compilation.
There are two types of adapter configuration files:
- Configuration files managed by Koupleless: During packaging, the koupleless-base-build-plugin plugin will attempt to pull the latest version of the adapter configuration file; if the pull fails, it will throw error and terminate. Currently, the open-source third-party package patches managed by Koupleless are in the koupleless-adapter repository, with over 20 patch packages available.
- User-defined configuration files: Users can add their own adapter configuration files to the base, and these configuration files will take effect alongside the general configuration files managed by Koupleless.
How to Develop Open-source Third-party Package Patches
👏 Welcome everyone to contribute to the development of open-source third-party package patches:
- Develop patch code files: Copy the files that need to be patched, modify the code to make it suitable for a multi-application scenario.
- Confirm the version range of the dependency package where the patch takes effect (i.e., within this version range, the code files of the open-source package are completely identical), for example, for org.springframework.boot:spring-boot versions within the range [2.5.1, 2.7.14], the
org.springframework.boot.logging.logback.LogbackLoggingSystemfile is the same. - In the koupleless-adapter repository, create a patch package module, such as
koupleless-adapter-spring-boot-logback-2.7.14, and overwrite the files that need to be patched in this module, for example,org.springframework.boot.logging.logback.LogbackLoggingSystem. - In the root directory of
koupleless-adapter-spring-boot-logback-2.7.14, create aconf/adapter-mappings.yamlfile to describe the matching rules for the patch to take effect, and complete unit tests. - Submit a PR
For example, the code for the koupleless-adapter-spring-boot-logback-2.7.14 patch package can be found at koupleless-adapter-spring-boot-logback-2.7.14.
How to Develop Internal Second-party Package Patches
- Develop patch code files: Copy the files that need to be patched, modify the code to make it suitable for a multi-application scenario.
- Confirm the version range of the dependency package where the patch takes effect (i.e., within this version range, the code files of the second-party package are completely identical), for example, for yyy:xxx versions within the range [2.5.1, 2.7.14], the
yyy.xxx.CustomSystemfile is the same. - Develop a patch package, such as
koupleless-adapter-xxx-2.1.0, and overwrite the files that need to be patched in this package, for example,com.xxx.YYY, and package and release it as a jar file. - Add the dependency configuration for the patch package in the base’s
conf/ark/adapter-mapping.yaml. For example:
adapterMappings:
- matcher:
groupId: yyy
artifactId: xxx
versionRange: "[2.5.1,2.7.14]"
adapter:
artifactId: koupleless-adapter-xxx-2.1.0
groupId: yyy
version: 1.0.0
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Welcome propose feedback to community!
Welcome propose feedback to community, or improve this document directly.。