2. Quick Start
Koupleless Quick Start
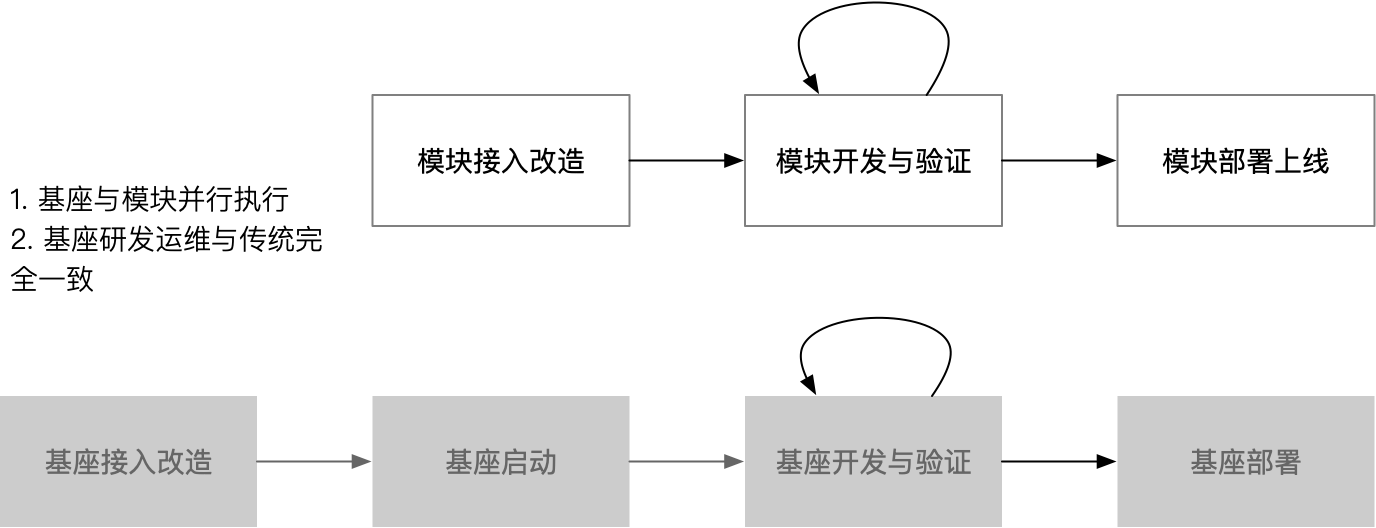
This quick start guide mainly introduces the dynamic merge deployment model, which is used to save resources and improve R&D efficiency. If you only want to save resources, you can use static merge deployment. This guide includes:
- Base Access
- Module Access
- Module Development Verification
- Module Deployment (not available yet, updates pending)
Video tutorials are also available, click here to view.
Prerequisites
- JDK 8, JDK 17, JDK 21+
- Maven v3.9.0+
- arkctl v0.2.1+, installation instructions can be found here
Operation and Maintenance Tools (not required for static merge deployment)
- Docker
- Kubectl
- K8s Cluster such as minikube v1.10+
Base Access
Refer to this link
Module Access
Refer to this link
Local Environment Development Verification
Check here
Module Deployment Example with Minikube Cluster (not available yet, updates pending)
Step 1: Deploy Operation and Maintenance Component ModuleController
kubectl apply -f xxx/xxx.yaml
Step 2: Publish Using Sample Base
- Deploy the base to the K8s cluster, create a service for the base, exposing the port,
you can reference here - Execute
minikube service base-web-single-host-service to access the base service
Step 3: Release the Module
There are two ways to release a module:
- Directly deploy the local module jar package to the K8s cluster
arkctl deploy ${path to the jar package} --pod ${namespace}/${podname}
- Deploy and release via K8s module deployment
Create a module deployment and use kubectl apply to publish
kubectl apply -f xxx/xxxxx/xx.yaml
Step 4: Test Verification
For More Experiments, Please View Sample Cases
Click here
1 - 2.2 Module Operations
Quick Start with Koupleless
This quick start guide mainly introduces Module operations based on Module Controller V2. It includes:
- Environment Preparation
- Module Controller V2 >= v2.1.3, Koupleless runtime >= 1.4.1-SNAPSHOT, SOFAArk >= 2.2.16
- Test Base Preparation
- Module Deployment and Status Checking
Environment Preparation
K8S Environment Deployment
Module Controller V2 builds Module operation capabilities based on K8S, so a basic K8S environment is needed first.
Note: Module Controller currently only supports arm64 / amd64 environments.
If you already have a K8S cluster, skip this section.
For local testing, it is recommended to use Minikube to quickly set up K8S locally. Minikube is an open-source tool for local Kubernetes deployment, helping quickly deploy K8S components.
To install Minikube, first, install the Docker environment: Docker Official Website
After installing Docker and starting the Docker daemon, Minikube installation preparation is complete.
Refer to the official documentation for Minikube installation.
Module Controller V2 Deployment
Module Controller V2 can be deployed in two ways:
- Local execution (requires go environment, not recommended)
- Image deployment (recommended)
Next, we will use image deployment as an example.
First, prepare necessary RBAC configuration for Module Controller V2.
- Download Service Account YAML
- Download Cluster Role YAML
- Download Cluster Role Binding YAML
Then apply the above three YAML files to set permissions and bindings for the service account.
Next, prepare the Pod Yaml for Module Controller deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: module-controller
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: module-controller
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: module-controller
spec:
serviceAccountName: virtual-kubelet # Service Account configured in the previous step
containers:
- name: module-controller
image: serverless-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/opensource/release/module-controller-v2:v2.1.4 # already upload to image registry
imagePullPolicy: Always
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1000m"
memory: "400Mi"
ports:
- name: httptunnel
containerPort: 7777
env:
- name: ENABLE_HTTP_TUNNEL
value: "true"
Apply the above YAML to the K8S cluster, and wait for the Module Controller Pod to reach the Running state.
The Module operations capability is now set up. Next, prepare the test base and test Module.
Test Base Deployment
To facilitate onboarding, a Docker image of a test base is provided. First, download the Base Yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: base
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: base
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: base
spec:
containers:
- name: base
image: serverless-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/opensource/test/base-web:1.4.0 # Pre-packaged image, from https://github.com/koupleless/samples/blob/main/springboot-samples/web/tomcat/Dockerfile
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- name: base
containerPort: 8080
- name: arklet
containerPort: 1238
env:
- name: MODULE_CONTROLLER_ADDRESS # which is `koupleless.arklet.http.heartbeat.endpoint` in koupleless runtime in the base-web
value: {YOUR_MODULE_CONTROLLER_IP_AND_PORT} # 127.0.0.1:7777
Replace {YOUR_MODULE_CONTROLLER_IP_AND_PORT} with the actual Module Controller Pod IP and Port in the YAML.
Apply the modified YAML to the K8S cluster and wait for the Base Pod to reach the Running state.
Once the base has started, verify its successful mapping to a VNode with:
If a node named vnode.test-base.dev appears and is Ready, the base is successfully started and mapped.
The UUID above is generated at base startup and changes each restart.
Next, use port-forward to expose the base container’s service for verification, using the command:
kubectl port-forward base 8080:8080
Visit link to verify if it maps successfully.
Module Deployment and Status Checking
Module Deployment
First, verify the state before Module installation by visiting the base service: Module Test.
It should return an error page indicating the Module is not installed.
Next, deploy the Module using a Deployment. Apply the Module YAML to K8S for Module deployment. Here is an example for a single Module, notice that the container name must be the same with the biz name defined in the jar:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: biz1-web-single-host
labels:
virtual-kubelet.koupleless.io/component: module-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
module: biz1-web-single-host
template:
metadata:
labels:
module: biz1-web-single-host
virtual-kubelet.koupleless.io/component: module
spec:
containers:
- name: biz1-web-single-host # this name must same with the biz name defined in the jar
image: https://koupleless-dosc.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/biz1-web-single-host-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-ark-biz.jar
env:
- name: BIZ_VERSION
value: 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
# these labels in vnode generated in base `https://github.com/koupleless/runtime/blob/main/arklet-core/src/main/java/com/alipay/sofa/koupleless/arklet/core/hook/base/BaseMetadataHookImpl.java`
# you can define your own labels by implementing your own BaseMetadataHookImpl
- key: base.koupleless.io/name
operator: In
values:
- TO_BE_IMPLEMENTED
- key: base.koupleless.io/cluster-name
operator: In
values:
- default
tolerations:
- key: "schedule.koupleless.io/virtual-node"
operator: "Equal"
value: "True"
effect: "NoExecute"
- key: "schedule.koupleless.io/node-env"
operator: "Equal"
value: "dev"
effect: "NoExecute"
Once deployment is complete, use kubectl get pods to check the status of all Module pods.
When the pods created by the deployment reach the Running state, the Module installation is complete. Verify by visiting the base service again: Module Test.
You should see the content: hello to /biz1 deploy, indicating the Module installation is complete.
Module Deletion
Modules can be removed by deleting their Deployment with:
kubectl delete deployment biz1
Check the pod deletion success with kubectl get pods.
After deletion, visit the base service Module Test to verify Module uninstallation.
The page should revert to the state indicating the Module is uninstalled.